Using Docker Swarm on AWS with Ansible & Terraform

Docker Swarm is an open-source container orchestration platform and is the native clustering engine for and by Docker. It allows you to manage multiple containers deployed across multiple host machines.
One of the key benefits associated with docker swarm is the high level of availability offered for applications. In a docker swarm, there are multiple worker nodes and at least one manager node that is responsible for handling the worker nodes’ resources efficiently and ensuring that the cluster operates efficiently.
Let’s start setting up our cluster in Terraform.
Verify your Terraform installation:
$ terraform --version
Terraform v0.14.2With Terraform (version 0.14.2 as of writing this) we can provision cloud architecture by writing code which is usually created in a programming language. In this case it’s going to be HCL — a HashiCorp configuration language.
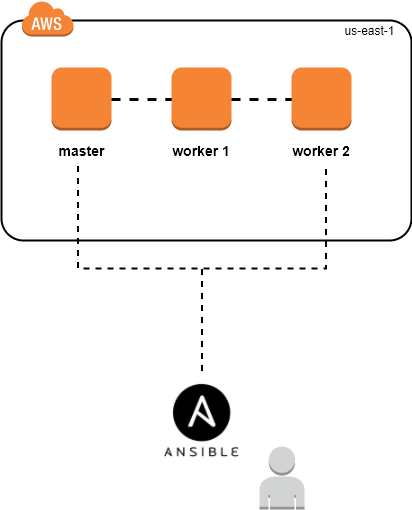
We are going to be setting up a Swarm cluster on AWS using Ansible and Terraform, refer to the diagram below. We will be setting up one Master node and two Worker nodes.
Global Variables
This file contains environment specific configuration AMI, Instance type, region, etc.
Configure AWS as our Provider
Set up Security Groups for inbound/outbound traffic.
Configure our EC2 Instances, Our Workers and Master
Next, our Bootstrap script to install the latest version of Docker
Transform to Swarm Cluster with Ansible, setting up the playbook
Everything is now complete and ready to initialize Terraform, Plan out the actions we are going to take, and then apply them to the cloud.
$ terraform init
$ terraform plan
$ terraform applyUpdate the /etc/ansible/hosts file with the public ip of each EC2 instance.
$ ansible -i hosts playbook.ymlI felt this was a good introduction to all of the tools involved. Thanks for reading.
I have uploaded all the files to GitHub.
